Calculating Precipitation Rates
Depending upon the construction of the irrigation system, the precipitation rate may be calculated by either a sprinkler spacing or a total area method.
Sprinkler Spacing Method
The precipitation rate should be calculated for each individual zone. If all sprinkler head on the zone have the same spacing, flow rate and arc of coverage.
i. Any Arc and Any Spacing

ii. Equilateral Triangular Spacing

Total Area Method
The precipitation rate for a system is the average precipitation rate of all sprinklers in an area, regardless of the spacing, flow rate or arc for each head. The total area method calculated all the flows of all heads in any given area.
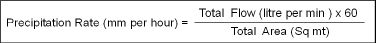
Matched Precipitation Rates
A zone or system in which all the heads have similar precipitation rates is said to have matched precipitation rates. Systems that have matched precipitation rates reduce wet and dry spots and excessive run times which lead to high water consumption and increased costs. Knowing that the sprinkler spacing, flow rates and arcs of coverage after precipitation rates, a general rule of thumb is : as the spray arc doubles, so should flow.
 ......90º Arc (Quarter Circle) - (0.23 m3/hr, 3.81 litre/min) ......90º Arc (Quarter Circle) - (0.23 m3/hr, 3.81 litre/min)
 …….. 180º Arc (Half Circle) - (0.45 m3/hr, 7.62 litre/min) …….. 180º Arc (Half Circle) - (0.45 m3/hr, 7.62 litre/min)
 ……...360º Arc (Full Circle) - (0.91 m3/hr, 15.24 litre/min) ……...360º Arc (Full Circle) - (0.91 m3/hr, 15.24 litre/min)
The flow rate of half circle heads must be two times the flow rate of the quarter circle heads and the full circle heads must have two times the flow rate of the half circle heads.
In the illustration, the same amount of water is applied to each quarter circle area and precipitation is therefore matched.
Types of Sprinklers based on Precipitation
| Type of Sprinkler |
Precipitation Rate (mm per hour) |
| Low Volume Sprinkler |
Less than 13 |
| Medium Volume Sprinkler |
13 - 25 |
| Big Volume Sprinkler |
Above 25 |
|